CHARA ALGAE
Chara
![]()
![]()
![]()
Class – Chlorophyceae
Order – Charales
Family – Characeae
Genus – Chara
Chara is commonly called as ‘ stone wort’ It is a submerged aquatic freshwater alga growing attached to the mud of the lakes and slow running streams. Chara baltica grows in saline water. The thallus is often encrusted with calcium and magnesium carbonate.
Thallus structure
The plant body is multicellular, macroscopic and is differentiated into main axis and rhizoids. The rhizoids are thread-like, multicellular structures arise from the lower part of the thallus or peripheral cells of the lower node.They are characterised by the presence of oblique septa. The rhizoids fix the main axis on the substratum and helps in the absorption of salts and solutes http://biologylibrarywith2023.blogspot.com
Reproduction
Chara reproduces by vegetative and sexual methods. Vegetative reproduction takes place by Amylum stars, Root bulbils, Amorphous bulbils and secondary protonema.
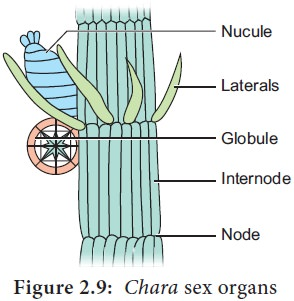
Sexual reproduction - Sexual reproduction is Oogamous. Sex organs are macroscopic and are produced on the branches of limited growth. The male sex organ is called Antheridium or Globule and the female sex organ is called Oogonium or Nucule (Figure 2.9). The Nucule is located above the Globule. The antheridium is spherical, macroscopic and its wall is made up of eight cells called shield cells. The antheridium has spermatogenous filaments. These filaments produce antherozoids. The nucule is covered by five spirally twisted tube cells and five coronal cells are present at the top of the nucule (Figure 2.9). The centre of the nucule
read more https://biologylibrarywith2023.blogspot.com/2023/02/phylum-porifera-structure.html









0 Comments